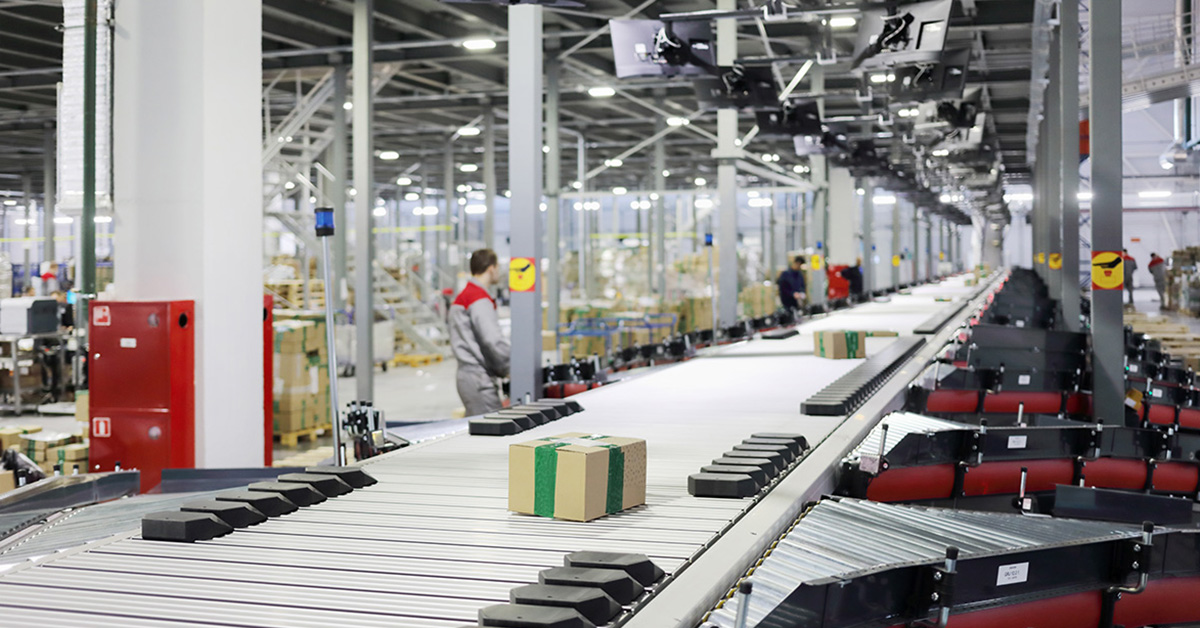
In a constantly changing world, warehouses operate under constant pressure and change. Warehouse leaders must balance the everyday concerns including warehouse efficiency, productivity, cost control, and meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
At the same time, they need the agility to respond quickly to disruptions and seize new opportunities when they appear. The challenge is that every process, from inventory control to order fulfillment, depends on data accuracy, visibility, and coordination across systems.
Mastering these daily activities by taking control of data creates the measurable gains and competitive advantages that effective warehouse management delivers.
What is Warehouse Management
Warehouse management is the strategic coordination of people, processes, and technology to move goods efficiently through the supply chain. It ensures that materials and products flow smoothly from receiving to shipping while maximizing space, time, and labor.
A warehouse management system (WMS) supports this coordination by connecting workflows, inventory data, and warehouse labor management in real time. Unlike traditional systems that only track transactions, a modern WMS turns warehouse data into actionable insights. This helps leaders see how every task, cost, and performance metric contributes to overall supply chain efficiency. Now that we understand how warehouse management brings order and insight, it’s time to see how the modern warehouse itself has evolved.
Modern Warehousing
Years ago, warehouses were designed mainly for storage with manual operating and record-keeping processes. Today they’re completely plugged in to technology and data. They serve as intelligent, connected hubs that link manufacturers, distribution centers, and fulfillment centers within the broader network of supply chain management.
Modern warehouse management focuses on real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and continuous optimization across systems. When executed well, it becomes a driver of profitability, customer satisfaction, and long-term competitive advantage.
The past 20 years have completely transformed how modern warehouses operate. The shift from paper and siloed systems to real-time digital visibility has been one of the most dramatic changes in supply chain management.
Today’s warehouses are powered by data. Automation, IoT sensors, labor management systems (LMS), and cloud-based warehouse management systems (WMS) connect every function, from receiving and inventory control to order fulfillment and shipping. These connected tools provide the visibility needed to manage labor efficiently, optimize space, and maintain an efficient supply chain across multiple distribution centers and fulfillment centers.
With predictive analytics and AI-driven forecasting, managers can anticipate demand shifts, plan warehouse labor proactively, and make smarter decisions before problems surface. This evolution is the foundation of modern warehouse performance management.
When leaders can see what’s happening in real time, they can respond faster, control costs, and turn visibility into measurable results across the entire operation. This sets the stage for understanding the processes that drive every warehouse’s success, from receiving to shipping.
Warehouse Management Processes
At the core of warehouse management systems are the daily activities that keep products moving through the facility. Every step, from receiving to shipping, offers an opportunity to improve warehouse efficiency, control costs, and strengthen visibility across the supply chain. When these processes are unified through data, they create the foundation of an efficient supply chain that can adapt quickly to change.
Here are some of the most common warehouse processes, and how unified data models have direct impacts on performance:
1. Receiving
The receiving process sets the tone for everything that follows. Accurate inbound handling ensures the right products enter the system in the right condition. A connected warehouse management system (WMS) can automatically verify purchase orders, log quantities, and flag discrepancies in real time. This visibility eliminates manual errors, reduces rework, and shortens unloading time. Some warehouses now use mobile scanning and automated dock scheduling to streamline the process, providing accurate data capture the moment goods arrive. A well-structured receiving workflow ensures every downstream process (inventory control, put-away, and order fulfillment) starts with reliable warehouse data.
2. Put-Away
Once materials are received, they must be placed in optimal storage locations. Data-driven routing and storage optimization algorithms reduce travel time and ensure space is used efficiently. By analyzing warehouse data such as SKU velocity, cube size, and frequency of picks, managers can assign the most efficient bin or rack location for each product. Advanced WMS platforms even recommend locations automatically based on item demand or temperature sensitivity, improving slotting in cold storage facilities and high-turn zones. Well-executed put-away processes increase warehouse efficiency, reduce congestion, and create the foundation for accurate picking and replenishment.
3. Inventory Control
Effective inventory control keeps stock levels accurate and ensures products are available when needed. Modern warehouses conduct regular inventory audits using barcoding technology, RFID, or automated cycle counting systems to maintain real-time visibility. Integrating these audits with a centralized WMS provides one accurate version of inventory across all systems, improving warehouse data management and forecasting. Many organizations now use predictive algorithms and AI to identify slow-moving SKUs and trigger FIFO system alerts. This helps reduce waste and carrying costs. Strong inventory control not only prevents costly stockouts but also contributes directly to overall supply chain efficiency.
4. Picking and Packing
The picking and packing process directly influences order accuracy, fulfillment speed, and customer satisfaction. Technologies such as pick-to-light, voice-directed picking, and mobile scanning reduce manual errors and increase throughput. When combined with detailed warehouse labor management data, supervisors can pinpoint inefficiencies such as excessive walking time or uneven workload distribution and address them in real time. Many operations also analyze pick path data and employee productivity to redesign zones or implement batch-picking strategies for faster order fulfillment. By connecting labor analytics with system data, warehouses can achieve better utilization and improved morale while reducing overall fulfillment costs.
5. Shipping and Logistics
Shipping is the final touchpoint before a product reaches the customer and the point where all previous processes are validated. Automation tools, barcoding technology, and integrated label printing ensure each order is correctly packaged, scanned, and confirmed. A connected WMS or transportation management system (TMS) communicates directly with carriers to generate tracking numbers and notify customers automatically. This data-driven process enables real-time visibility across distribution centers and fulfillment centers, helping teams identify bottlenecks and optimize dock scheduling. When shipping runs efficiently, it reduces delivery errors, improves customer satisfaction, and supports a resilient, efficient supply chain.
6. Value Added Services
Value added services include activities like kitting, labeling, assembly, customization, and returns processing that extend beyond standard warehouse workflows. While these services create differentiation and customer value, they are often highly variable and difficult to manage without consistent data. When value added services are treated as core warehouse processes and captured within a unified data model, operations gain clear visibility into labor effort, time, and workflow impact. This enables leaders to standardize execution where possible, staff accurately, forecast demand, and identify inefficiencies that would otherwise remain hidden. With unified data, value added services shift from unpredictable exceptions to measurable, controllable processes that improve efficiency, scalability, and overall warehouse performance.
Benefits of Warehouse Management
Effective warehouse management strengthens every link in the supply chain, creating measurable gains in accuracy, productivity, and cost control. When processes and systems work together, visibility improves and operations run with greater confidence and precision.
Accuracy and Control
Better inventory control reduces stockouts, mis-picks, and waste. This ensures the right products are always available.
Labor Efficiency
Tracking performance and balancing workloads improve warehouse labor management and overall productivity.
Speed and Service
Optimized workflows and real-time data visibility support faster order fulfillment and higher on-time delivery rates.
Cost Savings
Greater space utilization, fewer errors, and reduced idle time drive long-term warehouse efficiency and profitability.
Visibility and Insight
Connected systems provide the analytics needed for smarter decisions and continuous improvement across facilities and distribution center management.
These benefits highlight why optimization matters, however, achieving them requires specific actions and modern tools that can help you make improvements to fully realize the benefits of warehouse management.
Ways To Improve Warehouse Management
As the saying goes, you can’t fix what you cannot see clearly. Improving warehouse management begins with visibility. When you know exactly where time, effort, and cost are being lost, you can make the most effective improvements that combine accurate data, clear processes, and empowered teams. The following strategies offer practical ways to turn insight into measurable results.
Identify Hidden Time
Many facilities lose 10–20% of total labor hours to unmeasured or indirect work. Tracking this “missing time” helps uncover hidden inefficiencies that limit throughput and profitability.
Unify Systems and Data
Integrating data from your labor management, ERP, and warehouse management tools creates a single source of truth. This unified view allows managers to link warehouse data to performance metrics such as cost per unit or order cycle time.
Leverage Real-Time Visibility
Dashboards and alerts give supervisors the ability to immediately act on performance changes. This reduces downtime and improves responsiveness across shifts or sites.
Balance Automation and People
Automation is most effective when it complements skilled labor. Tools such as robotics, automated storage and retrieval systems, and pick-assist technologies can handle repetitive work while employees focus on higher-value tasks.
Benchmark and Continuously Improve
Compare results across facilities to set achievable targets for productivity, accuracy, and labor efficiency. Consistent benchmarking builds a culture of accountability and continuous improvement.
According to Gartner, warehouses that combine automation and data analytics improve productivity by up to 25% while reducing errors by more than 30%.
(Source: Gartner – Warehouse Automation Strategies and Optimization)
For example, a national 3PL achieved a 15% reduction in warehouse labor costs after connecting data from its labor management and inventory systems into a unified dashboard. The next evolution for many organizations is adopting a warehouse management system (WMS). A WMS can link these insights together to make every process more measurable, visible, and efficient.
The next logical step is understanding the role of warehouse management systems (WMS) and how they connect these improvements into one cohesive platform.
What Is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A warehouse management system (WMS) is a digital platform that organizes, tracks, and optimizes every stage of warehouse operations. It connects warehouse data across people, processes, and technology. It links tasks such as receiving, inventory control, picking, packing, and order fulfillment into one coordinated flow. By replacing manual spreadsheets and disconnected tools, a WMS helps companies gain accuracy, visibility, and speed across the supply chain.
Modern WMS platforms go far beyond simple inventory tracking. They use automation, barcoding technology, and automated storage and retrieval systems to streamline operations and minimize human error. When combined with real-time dashboards, they give managers the ability to see where products, people, and equipment are performing at their best and where to make improvements. The result is greater warehouse efficiency and a more efficient supply chain overall.
Yet even the most advanced WMS platforms have limits. They manage workflows and transactions, but they don’t always measure labor productivity or connect cost data across multiple systems. That’s why many organizations pair a WMS with warehouse performance management or analytics platforms – these are tools designed to unify data from WMS, labor management, and financial systems into a single, actionable view.
By layering deep analytics over the data already captured by your WMS, Warehouse performance management or analytics platforms help uncover hidden costs, quantify performance, and turn visibility into measurable results.
What to Look for in a WMS
Knowing what a WMS can and cannot do helps guide the search for the right solution platform and the right provider.
When evaluating warehouse management systems, look beyond product features or dashboards. The best solutions come from partners who understand the everyday realities of warehouse operations such as light margins, unpredictable demand, and the pressure to do more with less.
A WMS should not only organize your data but also help you interpret it to drive measurable warehouse efficiency and supply chain performance.
Look for a provider with both proven technology and real-world operational experience. Companies that bring together deep expertise in warehouse performance, advanced data analytics, and enterprise scalability are the best partners to help organizations connect their systems, people, and processes into one intelligent framework.
When comparing systems and providers, consider these key attributes:
Enterprise-Ready Scalability: A platform built to support operations across multiple distribution centers, fulfillment centers, or global networks. Look for enterprise-grade security, flexibility, and the ability to manage complex workflows consistently across locations.
Integrated Labor and Performance Insights: The most effective WMS solutions pair operational visibility with performance analytics. Platforms that incorporate warehouse labor management and benchmarking tools help identify opportunities, reduce cost per unit, and continuously improve productivity.
Engineered and Data-Driven Standards: Modern platforms go beyond static metrics. Look for systems that use dynamic, data-driven labor standards and are supported by machine learning and precise engineered models to make sure you can measure the true cost and performance of every activity.
Real-Time Visibility and Open Connectivity: Choose systems that unify warehouse data management, automation, and analytics across your technology stack through open APIs and seamless integration.
The right warehouse management system unifies operational data and human performance into a single source of truth. This helps transform warehouse operations into a scalable, data-driven advantage. It’s not just about running your warehouse more efficiently. You need a solution that creates the visibility that drives continuous improvement and lasting profitability.
Explore how connected data, analytics, and performance benchmarking can elevate your operation. Visit Easy Metrics Products to see solutions built for enterprise scalability, world-class labor management, and data-driven operational excellence.
Other Warehouse Management Resources
No single platform can do everything on its own. Many organizations complement their primary warehouse management systems with specialized technologies that extend automation, equipment, or analytics capabilities.
To expand capabilities according to individual organizational needs, Easy Metrics partners with trusted industry leaders like Generix and Raymond Corporation. Our partners are known for advancing warehouse automation, material handling, and distribution center management solutions. Together, these partnerships help facilities connect data, systems, and equipment into one coordinated ecosystem.
Across our customer base, we see consistent results when data visibility and performance analytics come together. For example, several national 3PLs and manufacturers using Easy Metrics have reduced labor costs by double digits and improved warehouse efficiency by linking their WMS data with real-time performance metrics.
Warehouse management today is about more than moving goods; it’s about continuous improvement through data visibility, actionable insight, and measurable performance. By integrating warehouse management systems with analytics platforms and real-time labor tracking, companies can strengthen supply chain efficiency, improve forecasting accuracy, and build long-term resilience across multiple facilities.
For additional insights on implementation and integration, visit our Frequently Asked Questions. And to see how data-driven visibility can transform your operation, explore Easy Metrics Products. Our solutions are designed to unify systems, measure performance, and accelerate warehouse improvement.
Final Thoughts on Warehouse Management
The future of warehousing is data-driven. As automation, AI, and connected systems continue to evolve, success will depend on how effectively organizations use warehouse data to make smarter, faster decisions. Warehouses that can see performance clearly across people, processes, and technology will lead the next era of supply chain management. With the right visibility and tools, every facility can transform from a cost center into a competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between warehouse management and warehouse operations?
A: Warehouse management oversees all activities within the facility, while warehouse operations refer to the day-to-day tasks that keep goods moving.
Q: What are the key benefits of using a WMS?
A: A WMS improves inventory control, storage optimization, order fulfillment, and overall supply chain efficiency.
Q: How does warehouse data improve performance?
A: By analyzing data across systems, companies can find inefficiencies, reduce missing time, and benchmark productivity.
Q: What technologies are shaping modern warehouse management?
A: Automation, AI, IoT, and predictive analytics are driving real-time decision-making and continuous improvement.
Q: How can I choose the right warehouse management system?
A: Look for a platform that integrates easily with your existing systems, offers real-time visibility, and is supported by a team with deep operational experience.